Payment processing has evolved into more than simply a convenience for small company owners in today’s quick-paced, digital environment.
It’s an essential stage in guaranteeing a smooth and effective transaction procedure, which can greatly increase sales and customer happiness.
We will delve into the complexities of payment processing for small business owners in this detailed tutorial, analyzing the different steps required in setting up and managing this crucial component of your enterprise.
Post Contents
1. Understanding Payment Processing
It is vital to have a solid understanding of the foundations of payment processing before getting into the specifics of the procedure.
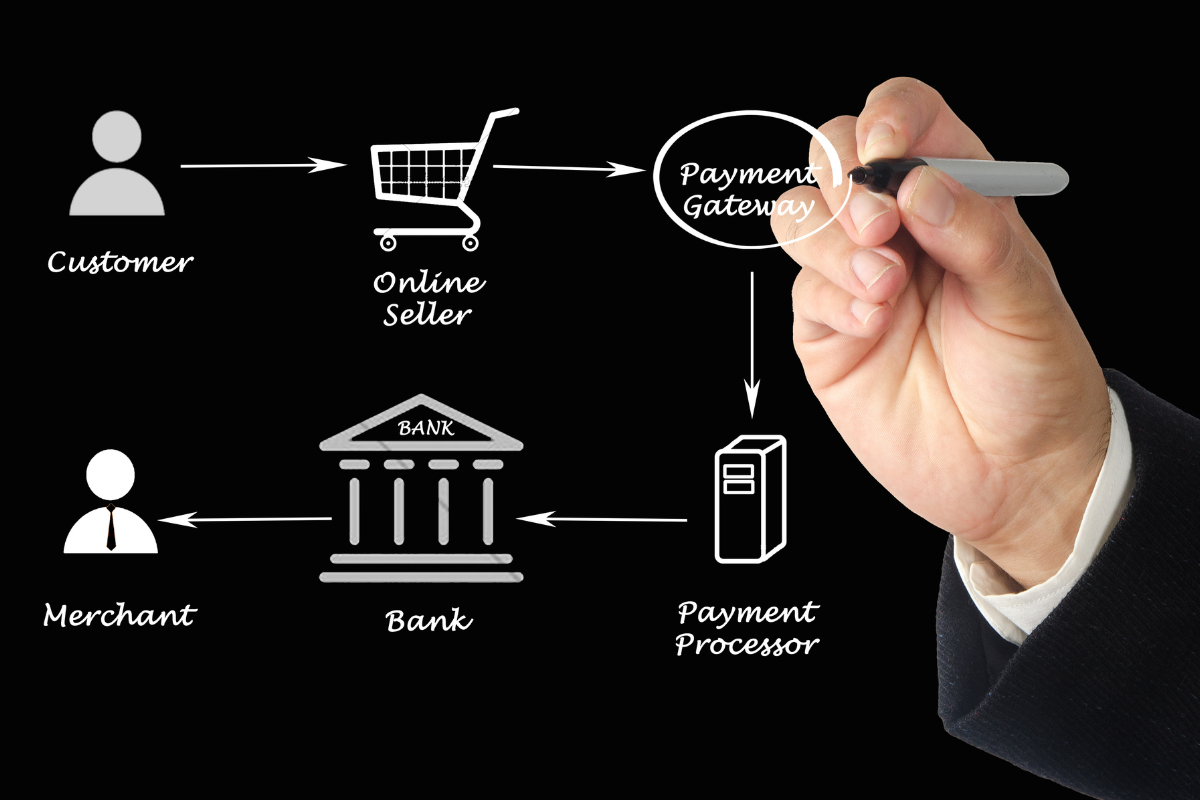
The whole system that enables businesses to receive payments from clients and manage those payments is referred to as payment processing.
This method requires participation from a number of different parties, including the client, the acquiring bank, the payment gateway, and the owner of the business.
2. The Role Of Payment Gateways
Payment gateways fulfill the role of middlemen between your company and the customer’s financial institution.
When a consumer enters their credit card information on your website or at one of your physical stores, the payment gateway encrypts the information. It sends it in a secure connection to the acquiring bank so that it can be authorized.
The payment gateway will, in the event that the transaction is successful, function as a middleman to facilitate the transfer of funds from the customer’s account to the business account.
3. Choosing The Right Payment Gateway
The choice of the appropriate payment gateway is an important decision that needs to be made by proprietors of small businesses.
There are a lot of different choices accessible, and each one has its own set of needs when it comes to features, prices, and how they should be integrated.
When selecting a payment gateway, it is important to think about a number of different elements, including the fees associated with transactions, the expenses associated with setup, the security features, and the compatibility with your e-commerce platform or point-of-sale system.
4. Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
When accepting credit card payments, it is crucial to guarantee the security of consumer data.
All companies that deal with credit card data must adhere to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
To prevent breaches of sensitive cardholder data, the PCI DSS establishes stringent security rules and regulations.
If you don’t follow these rules, you risk facing harsh penalties and harming your company’s reputation.
5. Integration With Your Business
Integration of a payment processing system into your business is a complicated but necessary step.
For your customers to have a seamless payment experience, it is crucial to be able to accept credit card payments through a trustworthy payment processing service that will protect personal information and provide security.
This entails linking your website or online store with the selected payment gateway for e-commerce firms.
Make sure the checkout procedure is simple to use and geared for mobile devices. A simple, straightforward payment process can lower cart abandonment rates and boost conversions.
Point-of-sale (POS) systems for physical stores must be compatible with the payment processing service you select.
It is simpler for business owners to manage in-store transactions with modern POS systems, which frequently have integrated payment processing capabilities.

6. Transaction Fees and Costs
Accepting credit card payments comes with costs, like processing fees. These charges frequently combine flat rates and a portion of each transaction.
The particular prices change according to the kind of credit card, the quantity of transactions, and your merchant account provider.
It’s important to comprehend the charge structure and look about for competitive rates to reduce costs.
Additionally, small business owners need to be aware of any additional expenses that can affect the overall cost of payment processing, such as chargeback fees, statement fees, or monthly minimums.
7. Payment Processing for Online Businesses
When accepting credit card payments, online firms in particular must put security and convenience first.
To stop fraudulent transactions, think about adopting extra security measures like two-factor authentication (2FA) and address verification systems (AVS) in addition to a secure payment gateway and PCI DSS compliance.
Additionally, giving clients a choice of payment methods might improve their buying experience.
To appeal to a wider client base, think about using digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Wallet in addition to credit card payments.
Conclusion
For small business owners hoping to succeed in today’s cutthroat marketplace, taking online payment is an essential step.
You can create a seamless payment experience that improves customer satisfaction and propels growth for your business by comprehending the nuances of payment processing, selecting the appropriate payment gateway and merchant account, prioritizing security and compliance, and offering first-rate customer support.
Keep in mind that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to payment processing. The best strategy for your company will depend on your unique requirements, sector, and clientele.
To remain competitive and adjust to shifting consumer demands, you should constantly evaluate and improve your payment processing strategy.