Owning a private plane symbolizes luxury and unparalleled freedom in travel. With over 15,000 private jets in North America, it represents the epitome of comfort and privacy in personal and business travel.
Bypassing crowded airports and having the liberty to create your flight schedules is a unique privilege that comes with such ownership.
However, this luxury demands a thorough understanding of maintenance and upkeep. Effective maintenance is crucial for safety and the aircraft’s longevity and value retention.
In private aviation, cutting corners is not an option. Meticulous upkeep preserves the prestige and security of your personal flying experience.
Post Contents
Understanding The Basics Of Aircraft Maintenance
Routine maintenance ensures the safety of the aircraft by regularly checking for and addressing any potential mechanical issues. This type of maintenance also prevents more extensive and costly repairs.
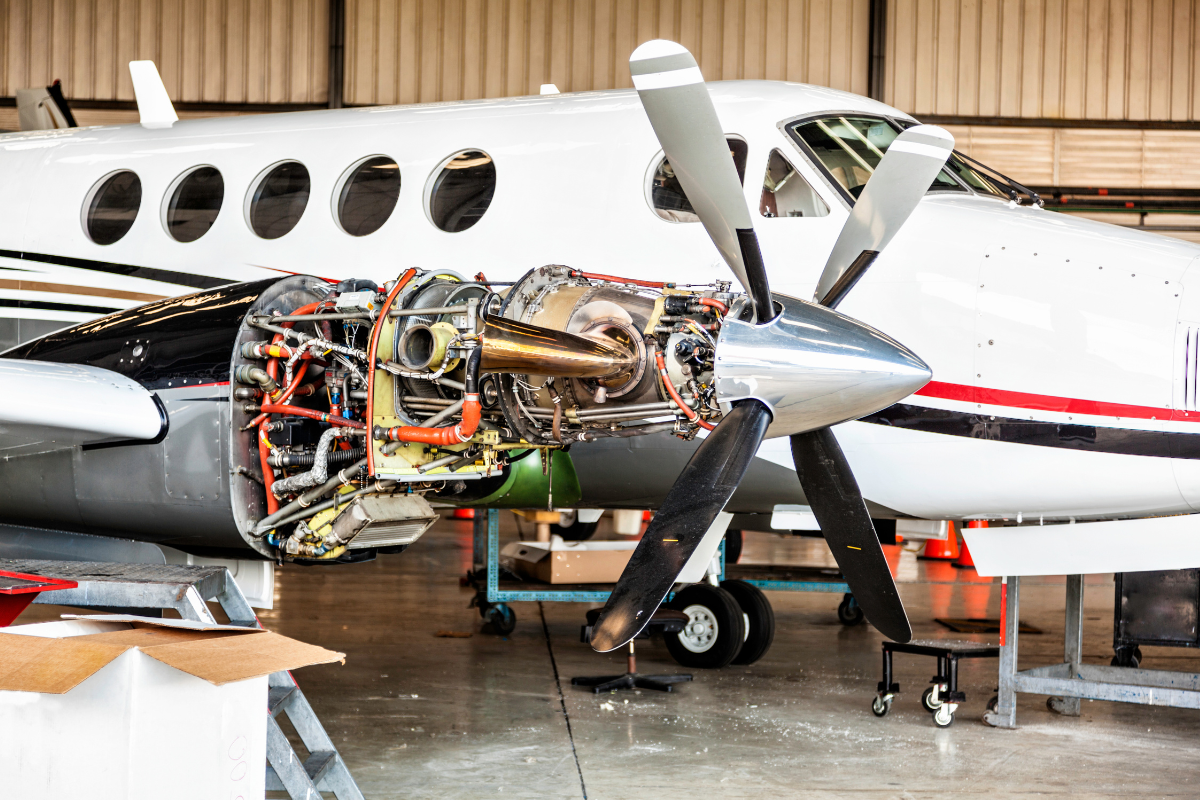

There are four main types of maintenance checks: A, B, C, and D.
- A Checks: These are the most frequent and least extensive checks, typically every 500-800 flight hours. They usually take a few hours and involve essential evaluations of the aircraft’s systems and components.
- B Checks: B checks are more thorough than A checks and occur every few months. They involve deeper inspections of various plane parts and can take up to a day or more to complete.
- C Checks: These checks are extensive and occur every 20-24 months. They require the aircraft to be taken out of service for a significant period, usually around one or two weeks. C checks involve thoroughly examining all components, including the airframe, engines, and onboard systems.
- D Checks: The most comprehensive and rigorous, D checks happen approximately every 5-10 years. They can take up to two months and involve a complete aircraft overhaul. It is when the plane is essentially taken apart and reassembled, ensuring everything meets the highest safety and performance standards.
The role of a certified aircraft mechanic is crucial in this process. These trained and licensed professionals carry out aircraft maintenance tasks.
They have the expertise to determine potential issues, perform necessary repairs, and ensure the aircraft meets all safety and regulatory standards.
They fix and prevent problems, ensuring the aircraft remains safe and reliable for every flight.
The Costs Of Maintaining A Private Plane
Breaking down the average maintenance costs for a private plane involves considering two main aspects: annual maintenance costs and costs per flight hour.
Annual maintenance costs can vary greatly depending on the type of aircraft. Annual maintenance might range from $600 to $1,200 for smaller, single-engine planes.
This figure can soar to $2,500 annually for larger, more complex jets.
Meanwhile, the cost per flight hour includes fuel, routine maintenance, and unforeseen repairs.
Depending on the aircraft’s size and complexity, it might cost $2,000 to $11,000 per flight hour or even higher.
Here are tips to save on maintenance costs:
- Regular inspections and preventive maintenance: Catching issues early can prevent more costly repairs later.
- Joining a maintenance program: Some programs offer cost-effective solutions for regular maintenance.
- Hiring a skilled maintenance team: Experienced mechanics can provide more efficient and effective service.
- Utilizing tax deductions: Certain maintenance expenses might qualify for tax deductions, which can reduce overall costs.
- Opting for fuel-efficient models: Choosing fuel-efficient planes can lower operating costs significantly.
Regulatory Requirements And Compliance
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) regulates private aircraft in the U.S. to ensure safety and security.

These regulations cover many areas, including pilot certification, aircraft maintenance, operations, and air traffic control.
For private aircraft owners, FAA regulations pertain to airworthiness standards, regular maintenance and inspections, flight rules, and pilot qualifications.
Compliance ensures the safety of both passengers and crew. Adhering to FAA standards minimizes the risk of mechanical failures and accidents.
Additionally, compliance is a legal requirement. Non-compliance can incur fines and suspension of the aircraft’s certification or the pilot’s license.
Therefore, staying within the boundaries of FAA regulations is essential for the legal and safe operation of private aircraft.
Staying updated with regulatory changes is vital as aviation regulations can evolve. Here are some ways to keep abreast of these changes:
- FAA website and publications: Regularly visit the FAA’s official website and subscribe to their publications for the latest information.
- Industry associations and groups: Join aviation associations that provide updates and resources.
- Training and continuing education: Engage in ongoing education and training programs, including updates on regulatory changes.
- Consultation with aviation experts: Regular consultations with aviation attorneys or consultants can provide insights into the latest regulatory changes and how they affect your operations.
Private aircraft owners can ensure a safe, legal, and enjoyable flying experience by staying informed and compliant.
Upkeep and Hangar Considerations
Proper storage in hangar facilities protects planes from environmental elements, which can damage the aircraft’s exterior and sensitive components.
They also provide security against theft and vandalism. Moreover, a hangar offers a controlled environment for maintenance and inspections, which is essential for keeping the aircraft in top condition.
When choosing a hangar, consider these factors:
- Location: Proximity to your home or business and ease of access to runways and airport facilities.
- Security: Look for hangars with robust security measures, including surveillance cameras, secure access points, and on-site security personnel.
- Amenities: Features like electricity, lighting, climate control, and access to maintenance tools can be crucial.
- Material: These provide durable, long-lasting protection for aircraft. For example, you can customize a steel hangar to fit specific size requirements. It is ideal for owners seeking a personalized aircraft storage solution that can withstand harsh weather conditions.
For effective aircraft cleaning and aesthetic upkeep, washing the exterior regularly to prevent corrosion is essential.
Likewise, apply protective coatings to guard against UV damage and keep the interior clean for comfort and hygiene.
Regular inspections during cleaning can help identify and address signs of potential wear or damage.
Professional cleaning and detailing services can also ensure a comprehensive job, especially for specialized materials or hard-to-reach areas.
These practices are vital in extending the life and maintaining the value of the aircraft.
Planning For Long-term Maintenance
Adhering to a well-structured maintenance schedule ensures the safety and longevity of a private aircraft, enabling timely identification and rectification of potential issues.
Financial planning for long-term upkeep is equally essential. It sets aside a dedicated maintenance fund or exploring options like maintenance insurance that can help manage costs effectively.
Proactive and informed maintenance planning, encompassing scheduled servicing and financial preparedness, avoids unforeseen expenses. It ensures the aircraft remains in peak condition, ready for safe and enjoyable flights.